Secret Detection (ULTIMATE)
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 11.9.
Overview
A recurring problem when developing applications is that developers may unintentionally commit secrets and credentials to their remote repositories. If other people have access to the source, or if the project is public, the sensitive information is then exposed and can be leveraged by malicious users to gain access to resources like deployment environments.
GitLab 11.9 includes a new check called Secret Detection. It scans the content of the repository to find API keys and other information that should not be there.
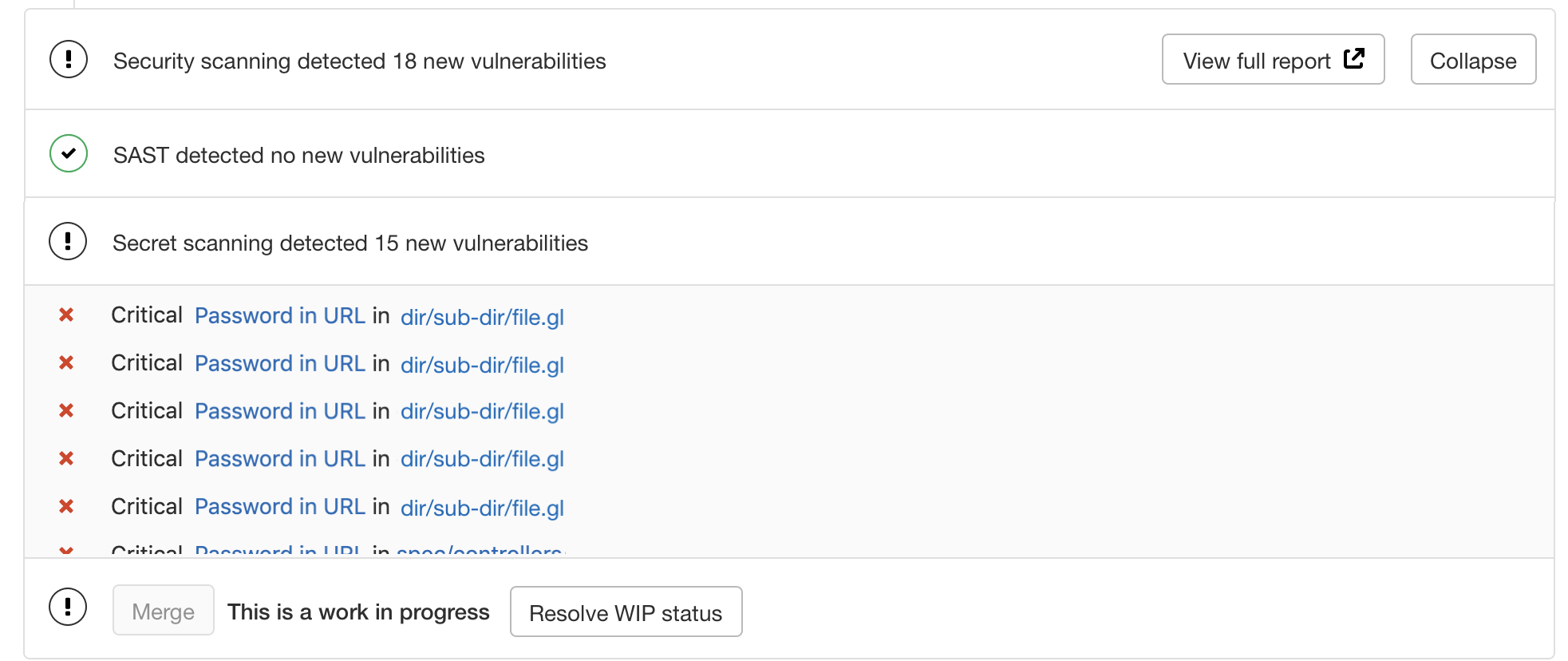
GitLab displays identified secrets as part of the SAST reports visibly in a few places:
- Security Dashboard
- Pipelines' Security tab
- Report in the merge request widget
Use cases
- Detecting unintentional commit of secrets like keys, passwords, and API tokens.
- Performing a single or recurring scan of the full history of your repository for secrets.
Requirements
To run Secret Detection jobs, by default, you need GitLab Runner with the
docker or
kubernetes executor.
If you're using the shared Runners on GitLab.com, this is enabled by default.
CAUTION: Caution: Our Secret Detection jobs currently expect a Linux container type. Windows containers are not yet supported.
CAUTION: Caution:
If you use your own Runners, make sure the Docker version installed
is not 19.03.0. See troubleshooting information for details.
Configuration
NOTE: Note: With GitLab 13.1 Secret Detection was split into its own CI/CD template.
Secret Detection is performed by a specific analyzer
during the secret-detection job. It runs regardless of the programming
language of your app.
The Secret Detection analyzer includes Gitleaks and TruffleHog checks.
NOTE: Note:
The Secret Detection analyzer will ignore "Password in URL" vulnerabilities if the password begins
with a dollar sign ($) as this likely indicates the password being used is an environment
variable. For example, https://username:[email protected]/path/to/repo won't be
detected, whereas https://username:[email protected]/path/to/repo would be detected.
NOTE: Note: You don't have to configure Secret Detection manually as shown in this section if you're using Auto Secret Detection provided by Auto DevOps.
To enable Secret Detection for GitLab 13.1 and later, you must include the Secret-Detection.gitlab-ci.yml template that’s provided as a part of your GitLab installation. For GitLab versions earlier than 11.9, you can copy and use the job as defined in that template.
Add the following to your .gitlab-ci.yml file:
include:
- template: Secret-Detection.gitlab-ci.ymlThe included template creates Secret Detection jobs in your CI/CD pipeline and scans your project's source code for secrets.
The results are saved as a Secret Detection report artifact that you can later download and analyze. Due to implementation limitations, we always take the latest Secret Detection artifact available.
Using the SAST Template
Prior to GitLab 13.1, Secret Detection was part of SAST configuration. If you already have SAST enabled for your app configured before GitLab 13.1, you don't need to manually configure it.
CAUTION: Planned Deprecation:
In a future GitLab release, configuring Secret Detection with the SAST template will be deprecated. Please begin using Secret-Detection.gitlab-ci.yml
to prevent future issues. We have made a
video to guide you through the process of transitioning
to this new template.
When using the SAST template, Secret Detection is performed by a specific analyzer
during the sast job. It runs regardless of the programming
language of your app, and you don't need to change your
CI/CD configuration file to enable it. Results are available in the SAST report.
Customizing settings
The Secret Detection scan settings can be changed through environment variables
by using the
variables parameter in .gitlab-ci.yml.
To override a job definition, (for example, change properties like variables or dependencies),
declare a job with the same name as the SAST job to override. Place this new job after the template
inclusion and specify any additional keys under it.
In the following example, we include the Secret Detection template and at the same time we
override the secret-scan job with the SECRET_DETECTION_HISTORIC_SCAN variable to true:
include:
- template: Secret-Detection.gitlab-ci.yml
secrets-scan:
variables:
SECRET_DETECTION_HISTORIC_SCAN: trueBecause the template is evaluated before the pipeline configuration, the last mention of the variable takes precedence.
CAUTION: Deprecation:
Beginning in GitLab 13.0, the use of only and except
is no longer supported. When overriding the template, you must use rules instead.
Available variables
Secret Detection can be customized by defining available variables:
| Environment variable | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
SECRET_DETECTION_COMMIT_FROM |
- | The commit a Gitleaks scan starts at. |
SECRET_DETECTION_COMMIT_TO |
- | The commit a Gitleaks scan ends at. |
SECRET_DETECTION_HISTORIC_SCAN |
false | Flag to enable a historic Gitleaks scan. |
Full History Secret Scan
GitLab 12.11 introduced support for scanning the full history of a repository. This new functionality is particularly useful when you are enabling Secret Detection in a repository for the first time and you want to perform a full secret scan. Running a secret scan on the full history can take a long time, especially for larger repositories with lengthy Git histories. We recommend not setting this variable as part of your normal job definition.
A new configuration variable (SECRET_DETECTION_HISTORIC_SCAN)
can be set to change the behavior of the GitLab Secret Detection scan to run on the entire Git history of a repository.
We have created a short video walkthrough showcasing how you can perform a full history secret scan.